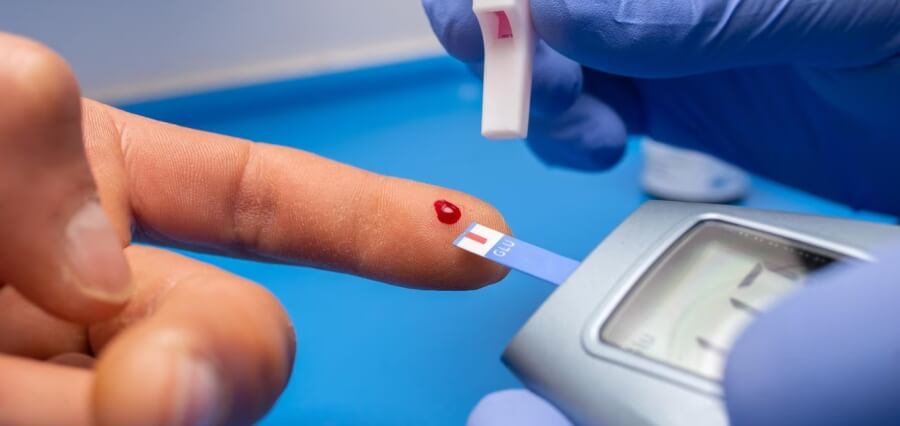
The European Diabetes Forum (EUDF)’s Stefano Del Prato and Bart Torbeyns discuss the main obstacles to diabetes management and prevention, as well as the steps that governments and healthcare systems may take to overcome them.
Diabetes is a global public health concern that raises healthcare costs and increases the risk of developing other non-communicable diseases.
More than 61 million individuals in Europe alone have diabetes, which is twice as many as in the previous ten years. A number of public health initiatives have been launched by the European Commission to assist diabetes prevention efforts and enhance information and support accessibility.
The European Commission introduced the “Healthier Together” non-communicable diseases program in 2021 with the goal of assisting EU Member States in enhancing citizen welfare and lowering the burden of NCDs.
A resolution on diabetes that calls for Member States to create, carry out, and oversee national diabetes plans and strategies was recently approved by the European Parliament.
Ensuring equal access to diabetes education, basic and secondary care, and therapies is the aim.
The European Diabetes Forum is a non-profit organization that was established in 2019 by the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation (JDRF), the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), the European Foundation for the Study of Diabetes (EFSD), and the Foundation of European Nurses in Diabetes (FEND) with the goal of affecting change at the policy level.
Following the launch, the International Diabetes Federation Europe (IDF Europe), the International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes (ISPAD), PCDE (Primary Care Diabetes Europe), and SFD (Société Francophone du Diabète) became members of EUDF. Pharmacies and medical technology firms are supportive collaborators of the EUDF.
We discussed the day-to-day difficulties of having diabetes, the role of digital solutions in enhancing care, and the legislative measures required to support early detection, address health disparities, and boost adoption of cutting-edge solutions with Bart Torbeyns, the Executive Director of the EUDF, and Chair Stefano Del Prato.
People with diabetes require care from a range of doctors in a range of settings (primary, secondary, and specialty care) throughout their life.
Thus, it’s imperative that healthcare professionals don’t give isolated, packaged treatments and that diabetic patients receive consistent care all the way through the system.
Promoting proactive preventative methods to enhance the experiences and results for individuals with diabetes requires coordinating treatment across services at various phases of the disease, including pre-diabetes, and maintaining regular and seamless interaction with the health system.
Implementing cost-effective processes within the health system and making judicious use of available resources are necessary to establish person-centered diabetes treatment.
Technological developments that enable digital access may make it simpler for patients to obtain health information and communicate it to their healthcare provider continuously, which could support patient-centered integrated care models.
Utilized in diabetes registries or diabetic information systems, diabetes-related health data produced by digitally enabled devices may enhance patient outcomes.
Technologies that can produce the necessary data and optimize self-care, as well as remote monitoring and treatment adjustments through the healthcare professional, while informing the health systems of performance and outcomes, include digitally enabled glucose monitoring systems, smart insulin delivery systems, algorithms, and medical apps.
Experts advise keeping an eye on blood sugar levels, exercising frequently (such as walking or playing), eating a healthy meal on time, and getting enough sleep. In the process, stress-reduction methods like yoga, meditation, and socializing are helpful.
Read More: https://thecareworld.com/